Elbow joint has stable bony structures, and be able to fulfil precise and skilful motions with delicate muscle groups.

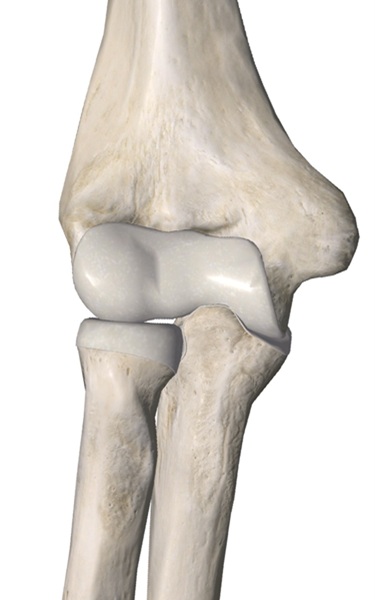
Elbow Joint Basic Anatomy
The elbow joints are formed by three bone: Humerus, Radius and Ulnar, articulate and form four joints: Superior Radio-ulnar Joint, Inferior Radio-ulnar Joint, Humeroulnar Joint and Humeroradial Joint. The elbow joints are further reinforced by joint capsule, ulnar collateral ligament and lateral collateral ligament.
There are 23 muscles in the elbow region, and it can be divided into four groups, including Elbow Flexor, Elbow Extensor, Flexor-pronator and Extensor-supinator. These muscle groups provide elbow with dynamic stabilising but at the same time facilitate forearm ability to fulfil skilful and precise mission.
Common Elbow Pain Reasons
Elbow pain can be caused by traumatic and overuse conditions. Elbow joint is relatively lesser wear and tear condition than other joint in the body. Soft tissue is prone to repetitive strain injuries. Here are several conditions common seen in the elbow causing pain.
• Tennis Elbow ( Epicondylitis )
• Golfer's Elbow ( Epicondylitis )
• Olecranon Bursitis
• Arthritis
• Ligament Sprain or Strain
• Radial Tunnel Syndrome
Tennis Elbow
Tennis elbow is the tendinopathy of extensor group over lateral epicondyle. It is originally named as "Medial Epicondylitis" in the literature. Extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB) is common soft tissue involved in the condition. ECRB would come across inflammation in acute stage, and it usually able to recover with proper resting. However, if the repetitive strain is still keeping, the tendon would then keep irritation and cause tendon degeneration. Tendinosis is therefore named, according to the histology found over the ECRB tendon.
Patient should rest their forearm and hand. No power grip is allowed in acute stage, and patient should not lifting heavy weight as it would encourage the synergistic contraction of forearm muscle.
How Traditional Chinese Medicine and Physiotherapy Help?
-
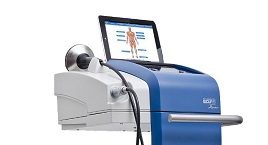 Focused Extracorporeal Shockwaves
Focused Extracorporeal ShockwavesRelieve pain and promote healing from chronic tendinitis
-
 Acupuncture and dry needling
Acupuncture and dry needlingAcupuncture is safe and effectively treat chronic neck pain.1
-
 Cupping therapy
Cupping therapyReduce pain, and improve function and quality of life.2
-
 Manual therapy
Manual therapyRelease muscle tightness, improve joint alignment and function.
-
 Chinese Herbal Remedy
Chinese Herbal Remedy
Nature way of Pain Killer, and improve sleep quality.
-
 Exercise Therapy
Exercise TherapyPromote injured tissue healing, improve the function of the affected area.
Reference:
- Yin, C., Buchheit, T.E., Park J.J.. (2017, October). Acupuncture for chronic pain: an update and critical overview. Current Opinion in Anaesthesiology , 30(5), 583-592. doi:10.1097/ACO.0000000000000501
- Liu, S., Wang, Z., Su, Y., Qi, L., Yang, W., Fu, M., Jing, X., Wang, Y., & Ma, Q. (2021). A neuroanatomical basis for electroacupuncture to drive the vagal–adrenal axis. Nature, 598(7882), 641–645. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04001-4