Low back refers to the lumbar region below rib cages, the pelvic region between two hip joints, and its' pain can also be the neuropathic origin.


Contributing factors:
- Lifting and moving: expected heavy weight lifting, especially with awkward postures.
- Fixed posture and prolonged sitting: causes static loading of soft tissues and causes discomfort.
- Sport injuries: over-exercises or be unfamiliarised with new equipment.
- Overexertion: under estimation of weight and overexertion of back muscle and soft tissues, easily injuries back.
- Traumatic event: Slippery floor or un-static platforms, easily twists and injuries lower back.
Treatment and prevention:
-
Self-care:
- Ice or hot pack: Initial 1 -2 days applying ice pack for 15 mins in every 4 hours, then 2 days afterward change to hot pack.
- Gentle stretching and mobilizing exercises: gently turn trunk within the pain-free range.
- Posture: keep up-right posture with back support.
- Lying with Supportive rolls : appropriate height towel rolls help keeping natural curvature of back bone during sleep.
- Self Massage: Gentle massage over lower back and buttock area, helps releasing muscle tightness.
-
Physiotherapy
- Electrotherapy
- Ultrasound
- Dry needling
- Shockwave therapy
- Manual therapy
-
Acupuncture
- Cupping therapy
What do the usual back problems' symptoms include?
- Back tightness with limited range of motions
- Prolonged sitting or standing would cause more back tightness and pain.
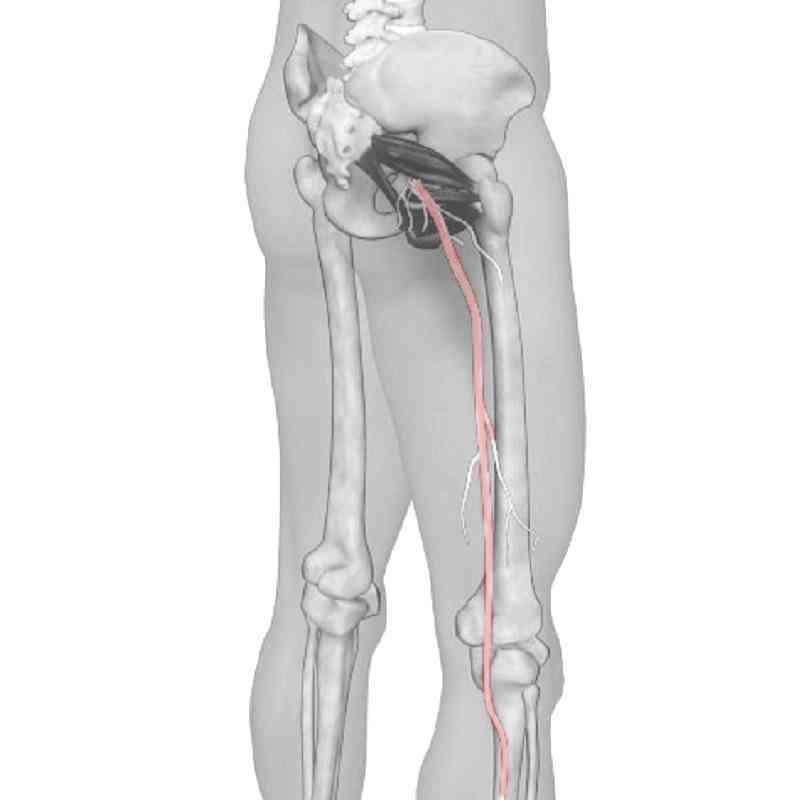
- Deep dull ach or pins and needles sensations propagate down the legs.
- Malalignment of upper back and finds centre of gravity lean to one side.
When to seek medical helps?
- Constant back tightness, not release with resting
- Persistent and explained leg soreness, or even weaknesses
- Inner thigh numbness or sudden onset of loss of bowel and bladder control.
Back basic anatomy explained: (pending)
The low back region covers the lumbar spine and part of the pelvic region. The lumbar spine is composed of five spine vertebrae, and body weight is distributed through the lumbar spine to pelvic and sacrum.
The low back stability is fulfilled by co-ordination of transverse abdominis and segmental tonic muscle.
Common causes:
Back pain can be deliberating, affecting up to 80% of the population suffering from significant back pain at some point during their life. There are certain factors predisposing for back pain, overweight, poor sitting posture, weak body muscle for keeping good spinal alignment, sitting for long time, etc. Most of the back pain cannot be diagnosed with clear pathology, and it would be marked as "Somatic Pain". However, there are few source that might be able to account for the most known reason of back pain.
- Sprained / Strained low back muscle
- Prolapsed Inter-vertebral Disc
- Sprained / Strained ligament
- Osteoarthritis
- Facet Syndrome
- SpondylolisthesisScoliosis
- Lumbar Stenosis
Intervertebral Disc Herniation, Protrusion, Extrusion, Sequestration
Intervertebral disc pathology has the progressive degree of displacement. Intact of annulus fibrosis and degree of nucleus pulpous displacement indicate the severity of intervertebral disc pathology.
Here is DO and DON'T for PID patients. Do beware of posture when PID is suspected or diagnosed; Don't bending forward with turning trunk, as it would further push nucleus pulposus displaced. Do sitting with supported upright posture, it would help to relieve pain and back muscle tightness; Don't sit on a sofa, as the collapsed sitting posture would further deteriorate the condition. Do core muscle training, it should start ASAP; Don't sit for a long time, or putting on corset for too long time, as it will weaken back muscle and make the back pain become chronic.
How Traditional Chinese Medicine and Physiotherapy Help?
-
 Focused Extracorporeal Shockwaves
Focused Extracorporeal ShockwavesRelieve pain and promote healing from chronic tendinitis
-
 Acupuncture and dry needling
Acupuncture and dry needlingAcupuncture is safe and effectively treat chronic neck pain.1
-
 Cupping therapy
Cupping therapyReduce pain, and improve function and quality of life.2
-
 Manual therapy
Manual therapyRelease muscle tightness, improve joint alignment and function.
-
 Chinese Herbal Remedy
Chinese Herbal Remedy
Nature way of Pain Killer, and improve sleep quality.
-
 Exercise Therapy
Exercise TherapyPromote injured tissue healing, improve the function of the affected area.
Reference:
1. Yin, C., Buchheit, T.E., Park J.J.. (2017, October). Acupuncture for chronic pain: an update and critical overview. Current Opinion in Anaesthesiology , 30(5), 583-592. doi:10.1097/ACO.0000000000000501.
2. Saha , F. J., Schumann, S., Cramer, H., Hohmann, C., Choi, K. E., Rolke, R., . . . Lauche, R. (n.d.). The Effects of Cupping Massage in Patients with Chronic Neck Pain - A Randomised Controlled Trial. Complementary Medicine Research, 24(1), 26-32. doi:10.1159/000454872.
3. Liu, S., Wang, Z., Su, Y., Qi, L., Yang, W., Fu, M., Jing, X., Wang, Y., & Ma, Q. (2021). A neuroanatomical basis for electroacupuncture to drive the vagal–adrenal axis. Nature, 598(7882), 641–645. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04001-4